
LEARNING STYLES IN ACTION
 LSA-Mini Complete
LSA-Mini Complete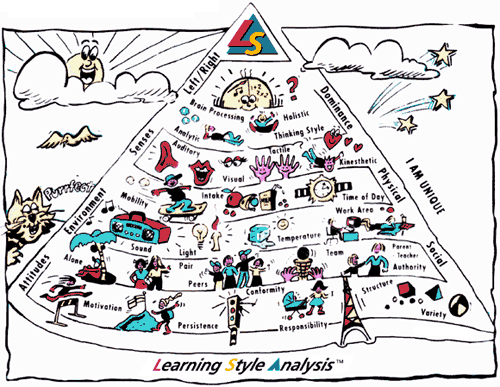
The LSA assesses 49 individual elements in the following six areas which are represented as layers of the pyramid. The first four of these layers can be described as biologically/genetically determined and the last two conditioned or learned:
LEFT/RIGHT BRAIN DOMINANCE | |
BrainReflective thinkers like time to consider everything before they make a decision, whereas impulsive thinkers make quick decisions based on little information. | 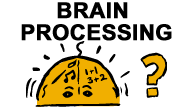 |
Analyticleft-brain dominant people prefer logical, step-by-step information, concentrate well on details and are highly sequential in taking in new information. | 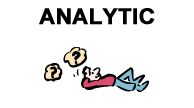 |
Holistic'right-brain' dominant people prefer to see the 'big picture' when learning new things, are not interested in details and process information simultaneously. |  |
SENSES | |
AuditorySome people remember things they hear, they are good listeners, like verbal instructions and/or prefer to discuss new information. |  |
VisualSome people remember much of what they read and prefer instructions to be written, others remember and understand best when shown pictures, others use their imagination and many a combination of these modalities. |  |
TactilePeople with this preference have a strong need to manipulate things and use their hands while listening or concentrating. |  |
KinestheticSome people like to be actively, physically involved in work projects and remember best through their own experiences; others have a strong intuition and need to feel good to understand and remember easily. |  |
PHYSICAL | |
MobilitySome people find it hard to sit still and need to move around a lot, especially when they are working or concentrating hard. Others prefer to stay put and avoid getting up when they work on something difficult. |  |
IntakeSome people work better when they nibble, eat or drink while concentrating, while others find it distracting when working on difficult tasks. |  |
TimePeople have different peak times when their brains are most active and then they can concentrate most easily. For some it's the early or late morning, for a few it's the afternoon and for many others it's the evening. |  |
ENVIRONMENT | |
SoundsSome people need it quiet when working on something difficult, others prefer sound or music in the background. |  |
LightSome people prefer bright light while others work far better in low light situations - too much light disrupts their concentration. |  |
TemperatureSome people like warm temperatures when working but others concentrate better when it's cool. |  |
WorkplaceStraight back chairs with desks suit a formal working style. Lounge chairs or lying on the floor when concentrating suit people with an informal working style. |  |
SOCIAL | |
AloneSome people concentrate best when allowed to work on their own. |  |
PairSome people prefer to have another person to work with. |  |
PeersSome people perform best when they can share their ideas and work within a group of like-minded people who are all at a similar level. |  |
TeamSome people love to be part of a team (sometimes as leader) and work most easily with others. |  |
AuthoritySome people accept authority and need very regular feedback, while others prefer not to have authority figures present, and don't need supervision. |  |
ATTITUDES | |
MotivationSome enjoy work, are self-starters and high achievers. Others can lose motivation easily, like incentives and need all other preferences matched to improve their work motivation. |  |
PersistenceSome people always finish what they begin while others stop when they lose interest and need frequent breaks and lots of encouragement to complete tasks. |  |
ConformitySome people need rules and regulations and always like to do what's 'right'; others follow their own rules and like doing unconventional things, often going 'against the stream'. |  |
ResponsibilityPeople who take responsibility do what's expected of them and consider the consequences of their actions carefully. Others don't consider work the most important thing in their lives, can be easily distracted from their duties and often forget what they promised. |  |
StructureSome people need clear guidelines and a framework to work within; others prefer to work independently without needing instructions. |  |
VarietySome people like change, variety and challenges, hardly ever doing the same thing twice. Others work better under routine and like predictability and steadiness in their work. |  |
 Mini Complete
Mini Student
Junior Complete
Junior Student
Swift Complete
Swift Student
Senior Complete
Senior Student
Adult
Mini Complete
Mini Student
Junior Complete
Junior Student
Swift Complete
Swift Student
Senior Complete
Senior Student
Adult
 Compare Editions
Compare Editions